Health Benefits Associated with Plain Greek Yogurt Consumption: Plain Greek Yogurt Nutrition Facts
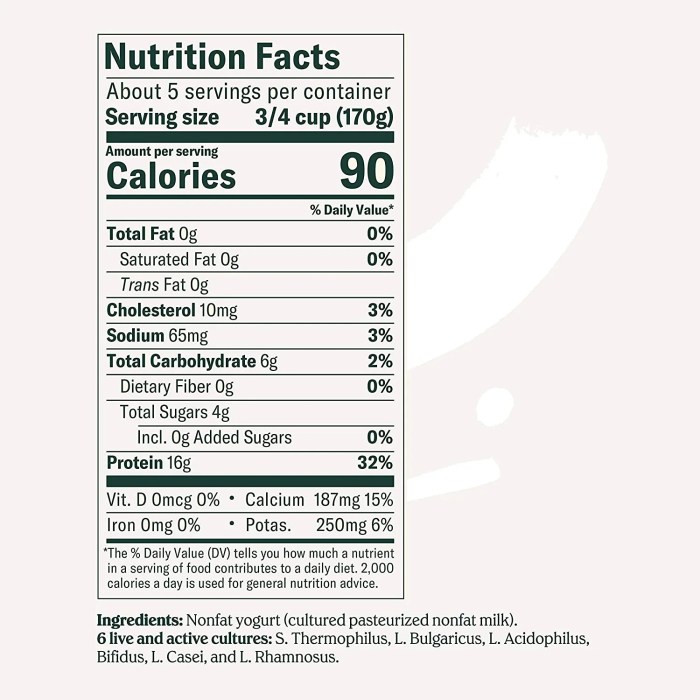
Plain greek yogurt nutrition facts – Plain Greek yogurt offers a wealth of nutritional benefits beyond its creamy texture and delicious taste. Its high protein content, rich calcium levels, beneficial probiotic bacteria, and varying fat profiles contribute to various aspects of health and well-being. Understanding these components allows for informed choices based on individual dietary needs and preferences.
Protein’s Role in Satiety and Muscle Building
Greek yogurt boasts a significantly higher protein content compared to many other dairy products. This high protein concentration contributes significantly to feelings of fullness and satiety, aiding in weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. A typical serving of plain Greek yogurt can provide between 15-25 grams of protein, depending on the brand and fat content. This protein is crucial for muscle building and repair, making Greek yogurt a valuable addition to any fitness regimen.
The essential amino acids present in the protein help the body synthesize new muscle tissue, promoting strength and overall physical performance. For example, a post-workout recovery smoothie incorporating Greek yogurt would provide both fast-digesting carbohydrates and sustained protein release for optimal muscle recovery.
Plain Greek yogurt boasts a high protein content and is a good source of calcium. For those seeking lean protein options, comparing its nutritional profile to other sources is beneficial; for example, you might want to check out the nutrition facts ground turkey offers. Ultimately, both are valuable additions to a balanced diet, though Greek yogurt often stands out for its probiotic benefits.
Calcium’s Contribution to Bone Health
Greek yogurt is an excellent source of calcium, a mineral vital for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Calcium is a key component of bone structure, contributing to bone density and reducing the risk of osteoporosis, particularly important as we age. Adequate calcium intake throughout life is crucial for preventing bone fractures and maintaining skeletal integrity. The calcium in Greek yogurt, combined with other nutrients like vitamin D (often added to fortified varieties), contributes significantly to overall bone health.
Probiotics and Their Impact on Gut Health
Many Greek yogurts contain live and active cultures, also known as probiotics. These beneficial bacteria contribute significantly to gut health by improving digestion, boosting the immune system, and potentially reducing symptoms of digestive disorders. Probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. A healthy gut microbiome is linked to improved overall health, including better digestion, reduced inflammation, and a stronger immune response.
Studies have shown that consuming probiotics regularly can improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other gastrointestinal issues.
Fat Content and its Influence on Nutrient Absorption
Plain Greek yogurt is available in various fat content options: full-fat, low-fat, and non-fat. Full-fat Greek yogurt contains higher levels of fat-soluble vitamins (like vitamins A, D, E, and K), which are better absorbed in the presence of fat. The fat content also contributes to a richer, creamier texture and increased satiety. Low-fat and non-fat varieties offer a reduced calorie and fat option, suitable for individuals managing their weight or cholesterol levels.
However, it’s important to note that fat-soluble vitamins may be less readily absorbed from low-fat and non-fat options. The choice between these options depends on individual dietary goals and preferences.
Plain Greek Yogurt in a Balanced Diet

Plain Greek yogurt is a highly versatile and nutritious food that can easily be incorporated into a balanced diet. Its high protein content contributes to satiety, aiding in weight management, while its calcium and probiotics support bone health and gut well-being. Understanding how to best utilize plain Greek yogurt in your daily meals can significantly enhance the nutritional profile of your diet.
Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Plain Greek Yogurt
The following meal plan demonstrates the diverse ways plain Greek yogurt can be included in a healthy eating pattern throughout the day. This is just a sample; individual needs and preferences will vary.
| Meal | Ingredients | Preparation Notes | Nutritional Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | 1 cup plain Greek yogurt, ½ cup berries, 1/4 cup granola | Combine all ingredients in a bowl. | High in protein, calcium, antioxidants, and fiber. |
| Lunch | Salad with 2 oz grilled chicken, mixed greens, vegetables, and 2 tbsp plain Greek yogurt dressing (yogurt, lemon juice, herbs) | Whisk together yogurt, lemon juice, and herbs for the dressing. Toss with salad ingredients. | Provides lean protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. Yogurt dressing offers a creamy alternative to higher-fat options. |
| Snack | 1 cup plain Greek yogurt with 1 tbsp chia seeds | Stir chia seeds into yogurt. Let sit for 10 minutes to allow chia seeds to absorb liquid. | Boosts protein and fiber intake, adding omega-3 fatty acids. |
| Dinner | Chicken and vegetable stir-fry with a side of plain Greek yogurt for dipping | Prepare stir-fry with lean protein and plenty of vegetables. Serve with plain Greek yogurt as a healthy, creamy dip. | Provides a balanced meal with lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and various vitamins and minerals. Yogurt dip adds protein and probiotics. |
Recipe: Savory Chicken and Yogurt Marinade
This recipe showcases plain Greek yogurt as a key ingredient in a flavorful and healthy marinade for chicken. The yogurt’s acidity tenderizes the meat, while its creamy texture contributes to a delicious final product.
Ingredients:
- 1 lb boneless, skinless chicken breasts, cut into 1-inch pieces
- 1 cup plain Greek yogurt
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tsp dried oregano
- ½ tsp paprika
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- In a medium bowl, combine all ingredients. Ensure the chicken is thoroughly coated in the marinade.
- Cover the bowl and refrigerate for at least 30 minutes, or up to 4 hours for maximum flavor.
- Grill, bake, or pan-fry the marinated chicken until cooked through.
Comparison of Plain Greek Yogurt with Other Dairy and Non-Dairy Alternatives, Plain greek yogurt nutrition facts
Plain Greek yogurt stands out nutritionally compared to many other dairy and non-dairy options. While variations exist depending on brand and fat content, generally, plain Greek yogurt boasts a higher protein content than most other yogurts and many milk alternatives. For example, compared to whole milk, Greek yogurt offers significantly more protein and less fat (depending on the fat content of the yogurt).
Compared to almond milk or soy milk, Greek yogurt provides a much higher protein content, although it may be lower in certain vitamins and minerals depending on the specific milk alternative. Cheese, while high in protein, often contains significantly more saturated fat than Greek yogurt. The probiotic content of Greek yogurt also sets it apart from many other dairy and non-dairy alternatives.
This is an important consideration for gut health.
Considerations for Plain Greek Yogurt Consumption

Plain Greek yogurt, while offering numerous health benefits, isn’t universally suitable. Certain factors, including individual dietary needs and preferences, should be carefully considered before incorporating it regularly into one’s diet. Understanding potential drawbacks and making informed choices are crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing any negative effects.Plain Greek yogurt’s nutritional profile, while generally positive, necessitates careful scrutiny of its ingredients and potential impact on specific health conditions.
The high protein content, while beneficial for many, might present challenges for others. Similarly, its lactose content requires consideration for individuals with lactose intolerance, while added sugars and other ingredients can significantly alter its nutritional value.
Lactose Intolerance and Dietary Restrictions
For individuals with lactose intolerance, consuming plain Greek yogurt can lead to digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, and diarrhea. The severity of these symptoms varies depending on the individual’s tolerance level and the amount of yogurt consumed. While some individuals with mild lactose intolerance may tolerate small portions of Greek yogurt, others may need to completely avoid it.
Those with more severe lactose intolerance or other dairy allergies should consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine appropriate dietary choices. Many lactose-free Greek yogurt options are available on the market, offering a suitable alternative for those with lactose sensitivity. These products undergo processing to remove lactose, allowing for dairy enjoyment without digestive distress. The nutritional content of lactose-free varieties might differ slightly from traditional Greek yogurt, so checking the nutrition label remains crucial.
Importance of Checking Nutrition Labels
Nutrition labels are essential tools for making informed decisions about food consumption. While plain Greek yogurt is generally considered a healthy choice, variations exist in terms of added sugars, fat content, and other ingredients. Some brands might add sweeteners, flavorings, or thickeners, altering the overall nutritional profile and potentially negating some of the health benefits associated with plain, unsweetened varieties.
Always check the nutrition facts panel to verify the amount of added sugars, total fat, saturated fat, and other ingredients. Opting for brands with minimal added sugars and no artificial ingredients is advisable for maximizing the nutritional benefits of Greek yogurt. For example, comparing two brands, one with 10g of added sugar per serving and another with 0g, highlights the significance of label checking.
The difference in sugar content can substantially impact overall health and weight management.
Dairy Alternatives for Limited Dairy Consumption
Individuals who need to limit or avoid dairy consumption due to allergies, intolerances, or personal dietary choices can explore several suitable alternatives. These include plant-based yogurts made from soy, almond, coconut, or oat milk. These options often provide a similar creamy texture and can be a good source of protein, though their nutritional profiles differ from dairy-based Greek yogurt.
For instance, soy yogurt is often higher in protein compared to almond or coconut yogurt. It’s crucial to compare nutrition labels to determine which alternative best meets individual nutritional needs. Other dairy-free options include silken tofu, which can be blended to create a yogurt-like consistency, or chia seed pudding, offering a different texture and nutritional profile. Choosing a suitable alternative depends on individual preferences and dietary requirements, and careful label reading is recommended.
Expert Answers
Can I eat Greek yogurt if I’m lactose intolerant?
Some individuals with lactose intolerance can tolerate Greek yogurt better than other dairy products due to the straining process, which reduces lactose content. However, lactose-free options are also available.
How does Greek yogurt compare to regular yogurt?
Greek yogurt generally has higher protein content and a thicker consistency than regular yogurt due to the straining process which removes whey. The nutritional values for fat and carbohydrates can vary depending on the type (full-fat, low-fat, non-fat).
Is Greek yogurt a good source of calcium?
Yes, Greek yogurt is an excellent source of calcium, crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth.
Does the fat content in Greek yogurt significantly impact its health benefits?
Full-fat Greek yogurt provides more calories and fat-soluble vitamins. Low-fat and non-fat versions offer fewer calories but may have slightly reduced nutrient absorption. The best choice depends on individual dietary needs and preferences.



