Sodium and Saturated Fat Content
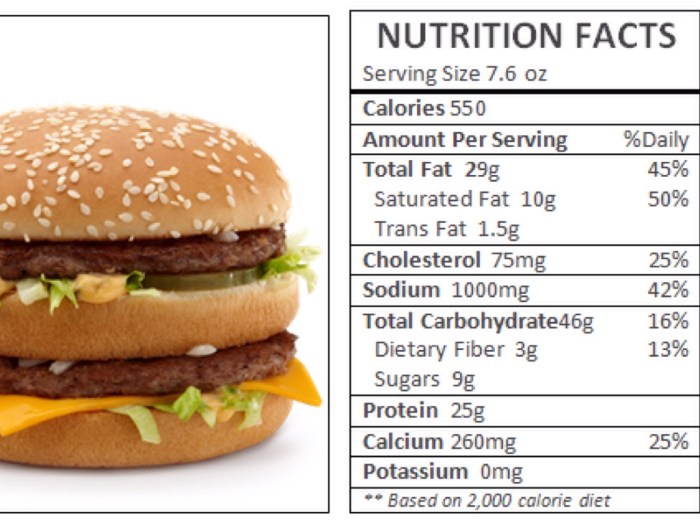
Nutrition facts on big mac – A Big Mac, a quintessential fast-food burger, contains a significant amount of sodium and saturated fat. Understanding these levels and their potential health effects is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section will detail the specific amounts present in a Big Mac and explore the associated health implications of consuming high levels of these nutrients.The sodium content of a Big Mac typically ranges from 970 to 1000 milligrams.
Saturated fat content usually falls between 11 and 13 grams. These figures represent a substantial portion of the recommended daily intake for most adults.
Understanding the nutrition facts on a Big Mac often involves comparing it to other convenient meals. For instance, a quick look at the cup of noodles nutrition facts provides a contrasting perspective on sodium and carbohydrate content. Returning to the Big Mac, its high fat and calorie count is a key consideration when assessing its nutritional profile.
Sodium and Saturated Fat Levels in a Big Mac and Daily Recommendations
The high sodium and saturated fat content in a Big Mac poses potential health risks. Excessive sodium intake is a major contributor to high blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Similarly, high saturated fat consumption is linked to elevated cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.To visualize the proportion, imagine a circle representing the recommended daily intake of sodium (approximately 2300mg).
A significant portion of that circle, perhaps around 40-45%, would be filled to represent the sodium in a single Big Mac. A similar circle representing the recommended daily intake of saturated fat (generally less than 20 grams for most adults) would show a large segment, perhaps 55-65%, filled to represent the saturated fat in one Big Mac. This illustrates the substantial contribution a single Big Mac makes to the daily intake of these nutrients.
Ingredient Analysis and Impact on Health

The Big Mac’s nutritional profile is a complex interplay of its various ingredients. Understanding these components individually and their collective impact is crucial for assessing its overall health effects. While a single Big Mac might not cause immediate harm, regular consumption raises concerns due to the high concentration of certain elements.
The Big Mac’s primary ingredients include beef patties, buns, special sauce, lettuce, cheese, pickles, and onions. Each contributes differently to the overall nutritional value (or lack thereof).
Individual Ingredient Nutritional Profiles, Nutrition facts on big mac
Let’s examine the key ingredients and their respective nutritional contributions. It’s important to note that precise nutritional values can vary slightly depending on sourcing and preparation.
- Beef Patties: A source of protein, but also contains saturated fat and cholesterol. The fat content contributes to the overall calorie density and can negatively impact cholesterol levels if consumed excessively.
- Buns: Primarily carbohydrates, providing energy but also contributing to blood sugar spikes. The refined flour used often lacks significant fiber, leading to a rapid rise in blood glucose.
- Special Sauce: High in fat and sodium. The mayonnaise-based sauce significantly contributes to the Big Mac’s calorie and fat content, further impacting cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Cheese: Provides protein and calcium, but also contains saturated fat and sodium. The type of cheese used influences the specific nutritional profile.
- Lettuce, Pickles, and Onions: These contribute some vitamins and minerals, but their nutritional impact is relatively minor compared to the other ingredients.
Combined Effect on Overall Health
The combined effect of these ingredients creates a meal high in calories, saturated fat, sodium, and refined carbohydrates. This combination poses several health risks with regular consumption. High saturated fat intake is linked to increased cholesterol levels, raising the risk of heart disease. The high sodium content contributes to hypertension (high blood pressure). The refined carbohydrates lead to blood sugar fluctuations, potentially contributing to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
The high calorie count, combined with the limited micronutrient density, contributes to weight gain and obesity.
Impact of Ingredients on Specific Health Aspects
Let’s look at the impact of specific ingredient groups on various health markers.
- Cholesterol Levels: The saturated fat in the beef patties, cheese, and special sauce significantly raises LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. For example, a study published in the
-American Journal of Clinical Nutrition* showed a clear correlation between high saturated fat intake and elevated LDL cholesterol. - Blood Sugar: The refined carbohydrates in the buns cause rapid spikes in blood glucose levels. This can lead to insulin resistance over time, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. A person with pre-existing diabetes might experience a particularly significant blood sugar spike after consuming a Big Mac.
- Blood Pressure: The high sodium content in the special sauce and cheese contributes to increased blood pressure. This increases the risk of stroke and heart disease. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend limiting sodium intake to reduce this risk.
User Queries: Nutrition Facts On Big Mac
How does a Big Mac compare nutritionally to other fast-food burgers?
Nutritional comparisons vary depending on the specific burger and restaurant. However, generally, Big Macs tend to be higher in calories, fat, and sodium compared to some other options, though not always significantly so. It’s important to compare specific nutritional information for accurate assessment.
Are there healthier alternatives to a Big Mac within the same restaurant?
Many fast-food chains offer healthier options, such as salads, grilled chicken sandwiches, or smaller portion sizes. Checking the nutritional information online or in the restaurant is recommended for making informed choices.
Can I eat a Big Mac and still maintain a healthy weight?
It’s possible to maintain a healthy weight while occasionally consuming a Big Mac. This requires balancing the higher calorie and fat content with other healthy food choices throughout the day and week. Regular exercise is also crucial.
What are the long-term health risks associated with frequent Big Mac consumption?
Frequent consumption of high-calorie, high-fat, and high-sodium foods like Big Macs increases the risk of weight gain, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other health problems. Moderation is key.



